
Let A = {2, 3, 4}, B = {6, 9, 12} and C = {a, b, c}. If f : A →
B and g : B → C are defined by f = {(2, 6), (3, 9), (4, 12)} and g = {(6, a),
(9, b), (12, c)},
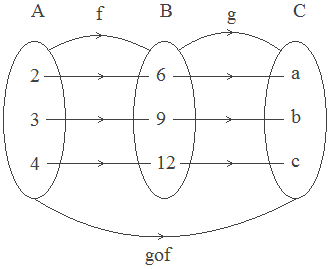
f is the function from A to B such that
2 ∈ A, f(2) = 6 ∈ B
3 ∈ A, f(3) = 9 ∈ B
4 ∈ A, f(4) = 12 ∈ B
Range of f = {6, 9, 12} = domain of g.
Again, g is the function from B to C such that
6 ∈ B, g(6) = a ∈ C
9 ∈ B, g(9) = b ∈ C
12 ∈ B, g(12) = c ∈ C
********************
10 Math Problems officially announces the release of Quick Math Solver and 10 Math Problems, Apps on Google Play Store for students around the world.
********************
********************
Now, a function defined from A to C such that
2 ∈ A, a = g(6) = g(f(2)) ∈ C
3 ∈ A, b = g(9) = g(f(3)) ∈ C
4 ∈ A, c = g(12) = g(f(4)) ∈ C
Then this new function defined from set A to set C is said to be
a composite function of f and g and
is denoted by gof or simply gf. Hence, we have (gof)(2) = a,
(gof)(3) = b, (gof)(4) = c.
Definition of Composite Function:
Let f : A → B and g : B → C be two functions. Then a new
function defined from A to C such that every element of A corresponds with a
unique element of C is known as the composite
function of f and g. It is denoted by gof
or simply gf.

Worked Out Examples:
Example 1: If f = {(2, 4), (6, 10), (8, 2)} and g = {(4, 6), (10, 2), (2, 6)},
then show that the function fog and gof in arrow diagram and find it in ordered
pair form.
Solution:
Here,
For fog
fog(4) = f(g(4)) = f(6) = 10
fog(10) = f(g(10)) = f(2) = 4
fog(2) = f(g(2)) = f(6) = 10
Hence, fog = {(4, 10), (10, 4), (2, 10)}
For gof,
gof(2) = g(f(2)) = g(4) = 6
gof(6) = g(f(6)) = g(10) = 2
gof(8) = g(f(8)) = g(2) = 6
Hence, gof = {(2, 6), (6, 2), (8, 6)}
Example 2: If f : R → R and g : R → R be the two functions defined by f(x) =
3x + 7 and g(x) = 2(x – 8), find gof(x) and fog(x) and test whether gof(x) =
fog(x) or not.
Solution:
Here,
f(x) = 3x + 7 and g(x) = 2(x – 8).
Now,
gof(x) = g(f(x))
= g(3x + 7)
= 2{(3x + 7) – 8}
= 2 (3x – 1)
= 6x – 2
∴ gof(x) = 6x – 2
And,
fog(x) = f(g(x))
= f(2(x – 8))
= f(2x – 16)
= 3(2x – 16) + 7
= 6x – 48 + 7
= 6x – 41
∴ fog(x) = 6x – 41
Hence, gof(x) ≠ fog(x)
Example 3: If f(x) = 2x – 1, g(x) = 3x and h(x) = x + 3, find
a. fogoh(x)
b. gofoh(2)
Solution:
Here,
We have, f(x) = 2x – 1, g(x) = 3x and h(x) = x + 3
a. fogoh(x) = f(goh(x))
=
f(g(h(x)))
= f(g(x
+ 3))
= f(3(x
+ 3))
= f(3x +
9)
= 2(3x +
9) – 1
= 6x +
18 – 1
= 6x +
17
b. gofoh(2) = g(foh(2))
=
g(f(h(2)))
= g(f(2
+ 3))
=
g(f(5))
= g(2 × 5
– 1)
= g(9)
= 3 × 9
= 27



0 comments: